Copyright © Hans Högman 2019-04-01


The Swedish Police of
Today
The Police Prior to 2015
Prior to 2015 the Swedish Police was
divided into 21 separate authorities, one for each
region, i.e. Län (county). Each Police region was
under the command of a County Chief Commissioner
(Länspolismästare).
The counties (Län) are an administrative regional
subdivision of Sweden. A US county is a local
subdivision so the US county shouldn’t be compared
to the Swedish county.
The National Police Board (Rikspolisstyrelsen) was
the central administrative authority, primarily tasked
with coordinating and supporting the local police.
The National Police Board was headed by a National
Chief of Police or National Chief Commissioner
(Rikspolischef) appointed by the government.
The police was organized under the Ministry of
Justice. Other law enforcement agencies
subordinated the National Police board was the
Security Service (Säkerhetspolisen), the National
Criminal Investigation Department (Rikskrim), the
Police Academy and the National Forensic Center
(Statens kriminaltekniska laboratorium (SKL)).
The Police Reform of 2015
In 2015 the different police authorities in each
region were consolidated into one authority, The
Police. The new authority was created to address
shortcomings in the division of duties and
responsibilities, and to make it easier for the
Government to demand greater accountability. The
agency is organized into 7 police regions and 8
national departments. With one police agency there
was no longer need for a National Police Board
which was abolished. The Police are now directly
subordinated the National Chief Commissioner
(Rikspolischef).
Concurrent with this change, the Swedish Security
Service (Säkerhetspolisen) formed its own agency.
The National Operations Department (Nationella
operativa avdelningen, NOA) is tasked with assisting
the local police regions and is in charge of
international police cooperation and all national
operations. The department has the power to
allocate extra resources, if needed, and has a
mandate to initiate nationwide operations and
activities. It is also responsible for investigating
crimes as prescribed by law to be conducted at the
national level, such as corruption and war crimes.
Furthermore, it handles all contacts with the
Swedish Security Service, Armed Forces and the
National Defense Radio Establishment, and
manages sensitive information about terrorism and
signals intelligence.
The National Task Force, NTF (Nationella
insatsstyrkan) is a police tactical unit within the
National Operations Department of the Swedish
Police Authority. The NTF handles extraordinarily
difficult or life-threatening criminal situations, such
as terrorism and hostage situations. The NTF also
conducts intervention tasks in cities too remote for
the reinforced regional task forces of Stockholm,
Gothenburg and Malmö, and too complex for the
regional task forces of the non-metropolitan regions
to handle.
The Swedish National Forensic Center (Nationellt
forensiskt centrum, NFC) is a Swedish government
agency, organized under Department of Justice as a
department of the Swedish Police Authority. It is
tasked with assisting the Swedish police in
investigating crimes.
The Swedish Security Service (Säkerhetspolisen,
SÄPO) is a Swedish government agency organized
under the Ministry of Justice. It operates like a
security agency responsible for counter-espionage,
counter-terrorism, as well as the protection of
dignitaries and the constitution. The Swedish
Security Service is also tasked with investigating
crimes against national security and terrorist crimes.
Its main mission, however, is to prevent crimes, and
not to investigate them.
Swedish government authorities enjoy a high degree
of independence. Neither the Government nor
individual ministers have the right to influence how
an agency decide in a particular case or on the
application of legislation. This also applies to the
Swedish police, who instead is governed by general
policy instruments, such as laws passed by the
Parliament (Riksdagen) and by the appointment of
executives.
Police Ranks as of 2015

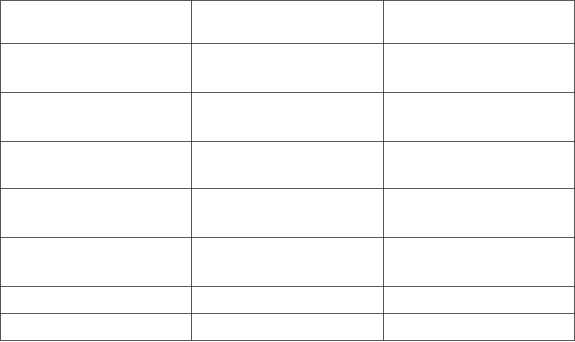
Swedish Police Ranks 2015 - Police Chiefs


Swedish rank
English
Comments
Rikspolischef
National Chief
Commissioner
National Chief of
Police
Regionspolisschef
(Polisdirektör)
Chief
Commissioner
Regional Chief of
Police
Biträdande
polisdirektör
Assistant
Commissioner
Assistant Police
Director
Polismästare
District Police
Commissioner
Police Area Chief
Polisöverintendent
Deputy Police
Commissioner
Police Senior
Intendant
Polisintendent
Chief
Superintendent
Police Intendant
Polissekreterare
Assistant
Commissioner
Police Secretary
History of the Swedish
Police
Police Rank Insignias 2015 - Police Chiefs
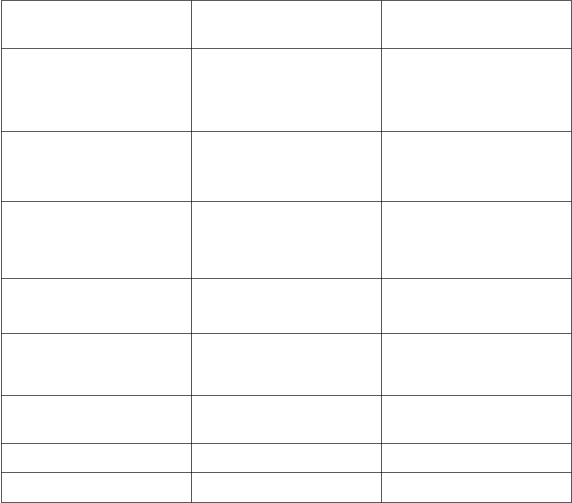
Swedish Police Ranks 2015 - Police Officers


Swedish Ranks
English
Comments
Poliskommisarie /
Kriminalkommissari
e
(Sektionschef)
Superintendent
(Section Chief)
Poliskommisarie /
Kriminalkommissari
e
Chief Inspector /
Detective Chief
Inspector
Polisinspektör /
Kriminalinspektör
(Gruppchef)
Inspector /
Detective Inspector
(Group Chief)
Polisinspektör /
Kriminalinspektör
Sergeant/
Detective Sergeant
Polisassistent
(4-years’
employment)
Senior Police
Constable
4 years’
employment or
more
Polisassistent
Police Constable
Less than 4 years’
employment
Polisaspirant
Police Trainee
Police Aspirant
Polisstudent
Police Student
Police Rank Insignias 2015 - Police Officers
Source References
•
Polisen i Stockholm förr och nu av Bengt Järbe,
1975.
•
Polisväsendet i Stockholm 1776 - 1850 av Nils Staf,
1950.
•
Din Polis, En orientering om polisväsendet på
landsbygden, utgiven av Malmöhus polisförening
1955.
•
Polisväsendet på landsbygden, Lundgrens förlag
Jönköping 1911.
•
Wikipedia
Top of page
Images
Swedish patrol car. Volvo V90 (2017).
Armored vehicle "Sandcat".
A CB90E fast assault craft used by the Swedish police.
This is a police version of the Amphibious Corps
combat boat CB90.
Length: 10.8m (35.4 ft), Beam: 2.90m (9.5 ft), Max.
speed: Approx. 42 knots.
The Amphibious Corps uses the bigger CB90H.
The Police headquarters, Kunsholmen, Stockholm.