Copyright © Hans Högman 2017-10-27
The Many Swedish
Wars - 1500s
Swedish Wars - 1500s
1521-1523, War with Denmark, "The War of
Liberation"
Allied with Sweden: Lübeck (from 1522).
Gustav Vasa of Sweden removed the Danish King
Christian II from the Swedish throne and drove the
Danes out of Sweden.
Gustav Vasa was elected new king of Sweden June 6,
1521 in the City of Strängnäs.
A few battles:
•
The battle of Västerås on April 29, 1521
•
The conquest Kalmar on May 27, 1523
•
The conquest Stockholm on June 16 - 17, 1523
After the capture of Stockholm, Sweden was again a
free nation. In September the Swedish Finland is also
liberated.
Peace in Malmö September 1, 1524.
1534-1536, War with Lübeck, "The
controversy of the count".
Allied with Sweden: Denmark and Prussia.
When King Frederik I of Denmark died in 1533 there
was a dispute about who the next king would be.
The foremost candidate was his oldest son, Duke
Christian. Another candidate was his younger son,
Hans.
A third candidate was the former king of Denmark,
Christian II. Christian II was forced to abdicate in
1523.
Count Christopher of Oldenburg (he actually gave
name to the controversy) was by force trying to
reinstate Christian II as King of Denmark.
At this time there was a conflict between Sweden
and Lübeck. After the Swedish Liberation War, which
ended in 1523, Sweden had large debts to Lübeck.
As a down payment of the debt Lübeck got a
monopoly of the Swedish trade (export and import).
The Swedish king, Gustav Vasa, didn’t really approve
of this and the relations between the two parts were
strained.
Now, Lübeck had plans to shut out the Netherlands
from the trade on the Baltic Sea. King Gustav Vasa
refused to support this, so did the Danes.
Lübeck now chooses to support Count Christopher
of Oldenburg in his efforts to reinstate Christian II as
the new king of Denmark.
Christian II was the opponent in the Swedish
Liberation War, and King Gustav Vasa did not wish to
see him back on the Danish throne. Therefore
Sweden decided to support Denmark with military
support against the Danish rebels supported by
count Oldenburg.
The combined Swedish-Danish forces did conquer
the rebels and Duke Christian was elected new King
of Denmark. As a king he was known as Christian III.
In 1536 Denmark signed a separate peace treaty
with Lübeck without notifying the Swedes. This
made King Gustav Vasa of Sweden furious and the
King immediately withdrew his troops from
Denmark.
Sweden signed an armistice with Lübeck on
November 25, 1636. The peace talks were resumed
in 1537 and a convention was signed in
Copenhagen on August 29, 1537. No formal peace
treaty was signed though.
The Swedish debt to Lübeck was now considered
settled and the Lübeck monopoly of the Swedish
trade ended.
Gain of land: +- zero
1554-1557, with Russia,"The Great Russian
War".
At this point in time, the relations between Sweden
and Russia had been very tense for a couple of
hundred years.
The Swedish expansion eastwards continued during
the regime of King Gustav Vasa.
The conflicts along the Swedish-Russian border
escalated into a war in the beginning of 1555.
Sweden was the aggressor in the war.
Peace in Novgorod April 2, 1557.
The terms were an armistice for 40 years and a
rectification of the borders. However, a rectification
was never carried out.
Gain of land: +- zero
1561
, The Submission of Estonia
The Estonian knighthood, including the city of Reval,
turns themselves into Swedish hands after a trial of
strength between Russia, Denmark, Sweden and
Poland-Lithuania.
The western part of Estonia, the
province of Wiek, falls into Swedish
hands in 1581.
Map of Sweden 1561
Gain of land: + Major part of Estonia
(the provinces of Harrien, Wierland
and Jerven) including the city of Reval
(today's Tallinn)
See detailed map
1563-1570, War with Danmark, Poland and
Lübeck "The Northern Seven Years' War"
In the Swedish Liberation War, which ended 1523,
the Swedes ended a period of Danish regents of
Sweden. Ever since that year, the Danes had tried to
recapture the Swedish throne.
This war was a new attempt to do so and was in
large a struggle for the domination of the Nordic
Region.
In the beginning of the war the Danes took the only
gateway Sweden had on the west coast, the Älvsborg
fortress.
A first attempt for peace was made in Roskilde,
Denmark, in November 1568.
The final peace treaty was signed in Stettin,
December 13, 1570. According to the treaty, Sweden
was to pay 150,000 riksdaler to Denmark to regain
Älvsborg, an enormous amount in those days. That
process was called "Älvsborgs lösen" (The Älvsborg's
ransom).
In the peace treaty, the Kalmar Union was formally
dissolved and the Danish king relinquish all claims of
the Swedish throne. For the first time Sweden
recognized the so called Skåne provinces (Skåne,
Blekinge and Halland) as Danish territory.
The Stettin peace also included a peace treaty with
Lübeck.
(Riksdaler was the Swedish currency at the time.)
Gain of land: - Sweden had to pay to get Älvsborg
back (A Swedish fortress on the west coast)
See detailed map.
1563-1568, War with Poland and the
Livonian nobility, "The First Polish War".
During the Nordic Seven Years' War (see above),
Poland supported the Danes. However the Polish
participation in the war ended when the Swedish
Duke Johan (Johan III) succeed his brother, Erik XIV,
on the Swedish throne in 1568. King Johan III was
married to a Polish princess. This war was foremost
fought in Livland (in the Baltic region).
There was no formal peace treaty with Poland.
Gain of land: +- zero
1570-1595, War with Russia. "The 25 Years'
War with Russia"
Allied with Sweden: Poland between 1578 and 1582.
In 1561 Sweden begun a powerful expansion to the
east. This expansion resulted in a conflict with
Russia. The aim for the Russians in the war was to
capture the Swedish provinces in the Baltic region.
The war started in 1570 when Russia and Poland
signed an armistice.
In 1581, Narva and the nearby city Ivangorod falls
into Swedish hands.
•
Armistice in Pliusa on August 10, 1583 (Sweden
possesses Estonia, Kexholms län and a large
part of Ingermanland (Ivangorod, Jama and
Kopore))
•
Armistice in Pliusa on December 19, 1585
•
Armistice in Narva on February 10, 1590
(Sweden retires from Ivangorod, Jama and
Kopore but keeps Narva and the part of Estonia
located west of river Veilika.)
•
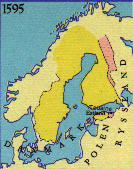
Peace in Teusina May 18, 1595. Sweden keeps
Narva and the whole of Estonia inclusive the city
of Reval. Russia receives the
major part of Ingermanland and
Kexholms län.
Landvinningar: + Narva (today an
Estonian city), + A part of
Ingermanland (Baltic province), + The
rest of Estonia (The Baltics), -
Kexholms län
Map of Sweden 1595
The borderline between Sweden and Russia are
established: From the Systerbäckens outlet in
eastern part of the Gulf of Finland, across the lakes
Saimen and Enare träsk, across Neugdona on the
Kola Peninsula and up to the Arctic Ocean.
See detailed map.
1598-1599, War with Poland, "The War with
Sigismund" (in Reality a Swedish Civil War)
Sigismund, King of Sweden as well of Poland, was
forced to give up the Swedish throne.
The battles of Stegeborg September 8 and of
Stångebro September 25, 1598 between Duke Karl
and Sigismund are well known.
Sigismund was the son of the Swedish King Johan III
in his marriage with the Polish princess Katarina
Jagellonica. When Johan III died in 1592 Sigismund
became King of Sweden. However there was a
problem. Sweden was a Lutheran nation since the
1520’s and Sigismund was of catholic faith plus King
of Poland since 1587. Duke Karl was a brother of
Johan III and therefore Sisgismund’s uncle.
There was also a conflict between Sweden and
Poland about Estonia. Those conflicts grew into a
war between Duke Karl and Sisgismund. Duke Karl
won this war and was in 1599 elected new King of
Sweden as King Karl IX.
Gain of land: +- zero